Human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV)
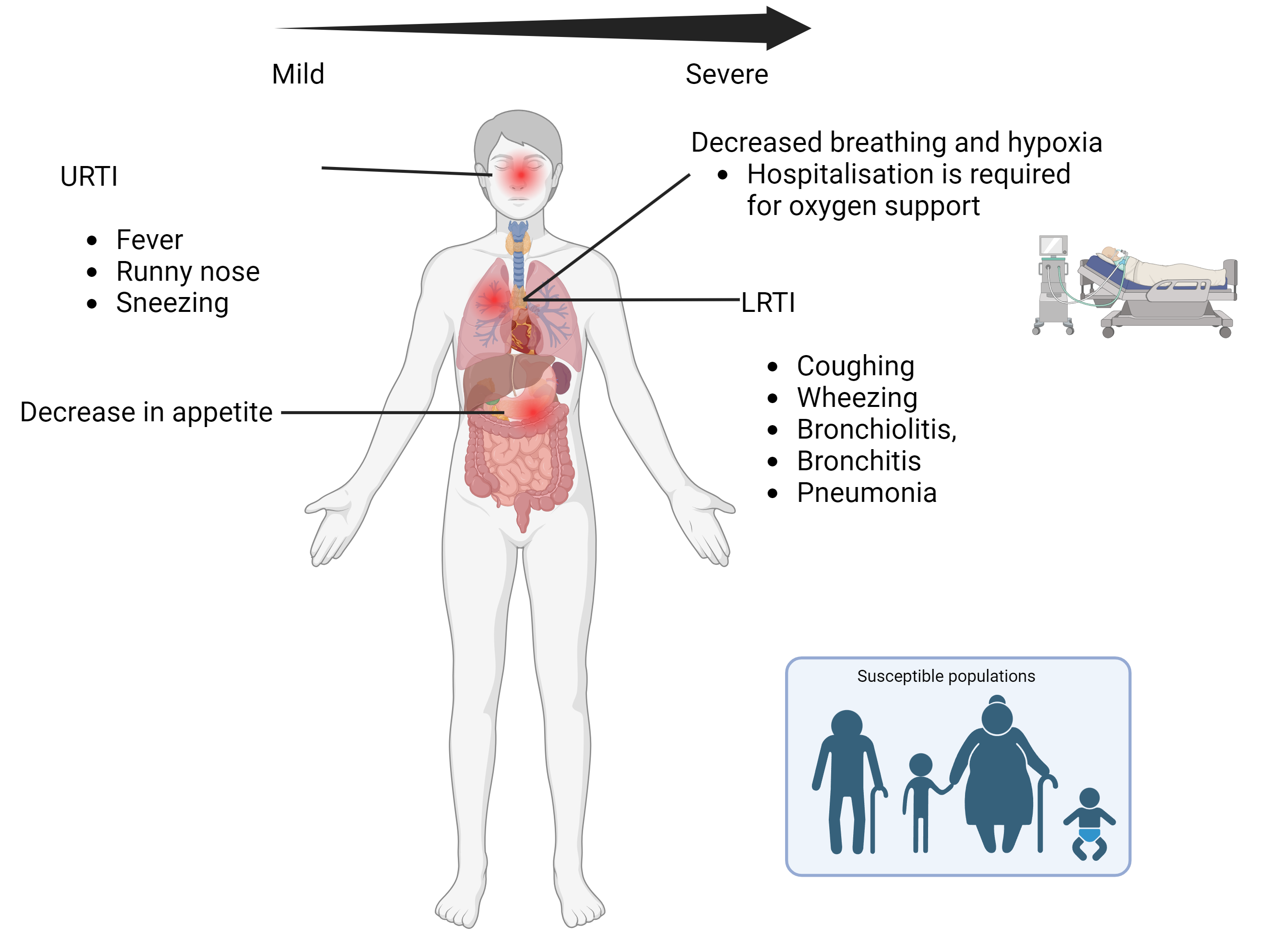
Respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV, is a common respiratory virus that usually causes mild, cold-like symptoms.
Most people recover in a week or two, but RSV can be serious, especially for infants and older adults.
RSV is the most common cause of bronchiolitis (inflammation of the small airways in the lung) and pneumonia (infection of the lungs) in children younger than 1 year of age in the United States.
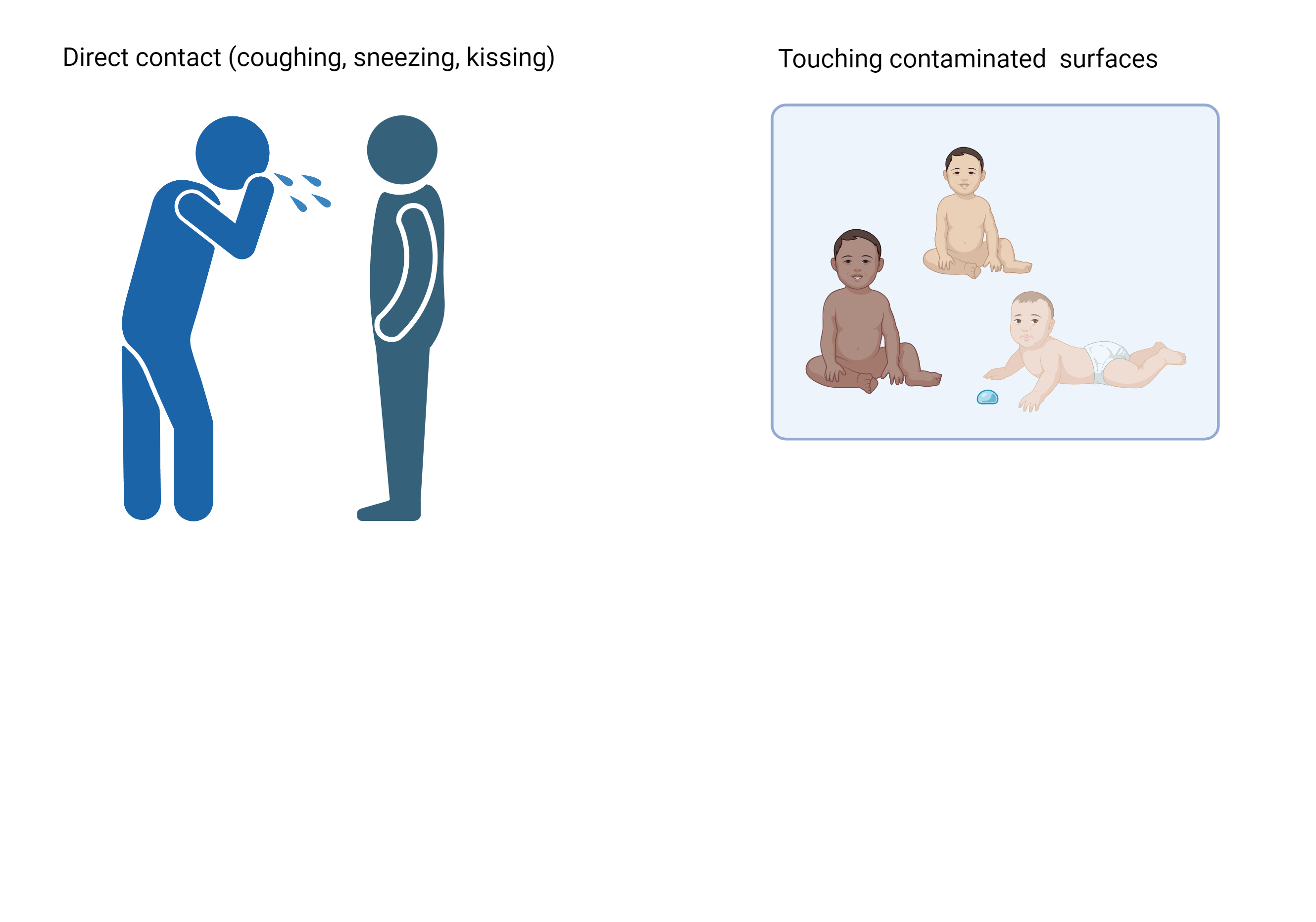
People infected with RSV are usually contagious for 3 to 8 days and may become contagious a day or two before they start showing signs of illness. However, some infants, and people with weakened immune systems, can continue to spread the virus even after they stop showing symptoms, for as long as 4 weeks.
RSV can survive for many hours on hard surfaces such as tables and crib rails. It typically lives on soft surfaces such as tissues and hands for shorter amounts of time.
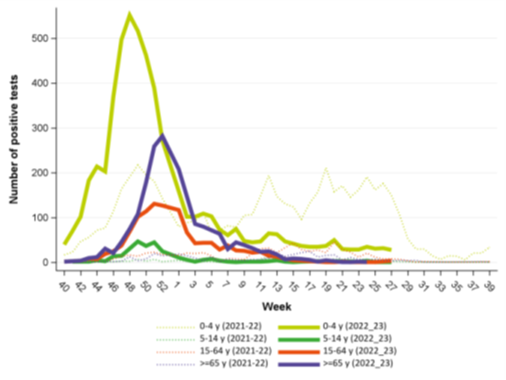
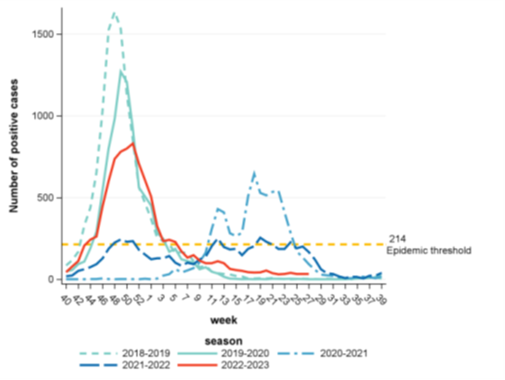
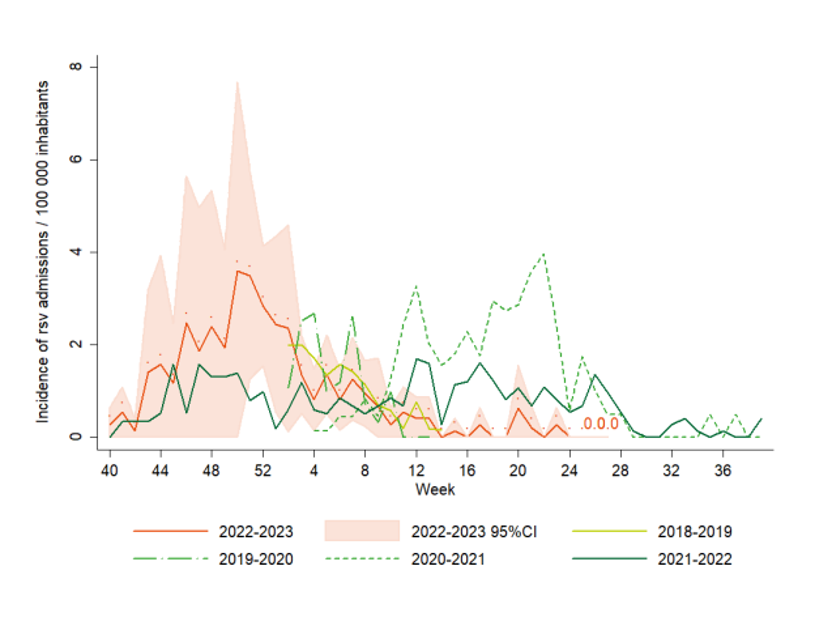
(Reference: Graphs pertaining to RSV seasonality in Belgium have been sourced from Sciensano.)