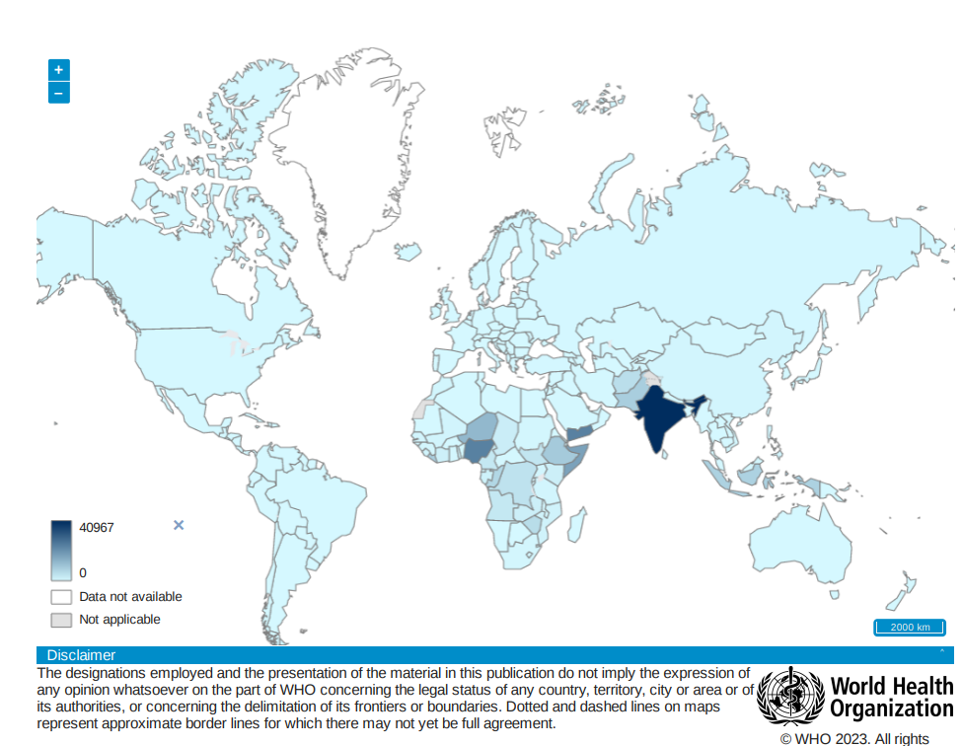
Measles virus (MeV)
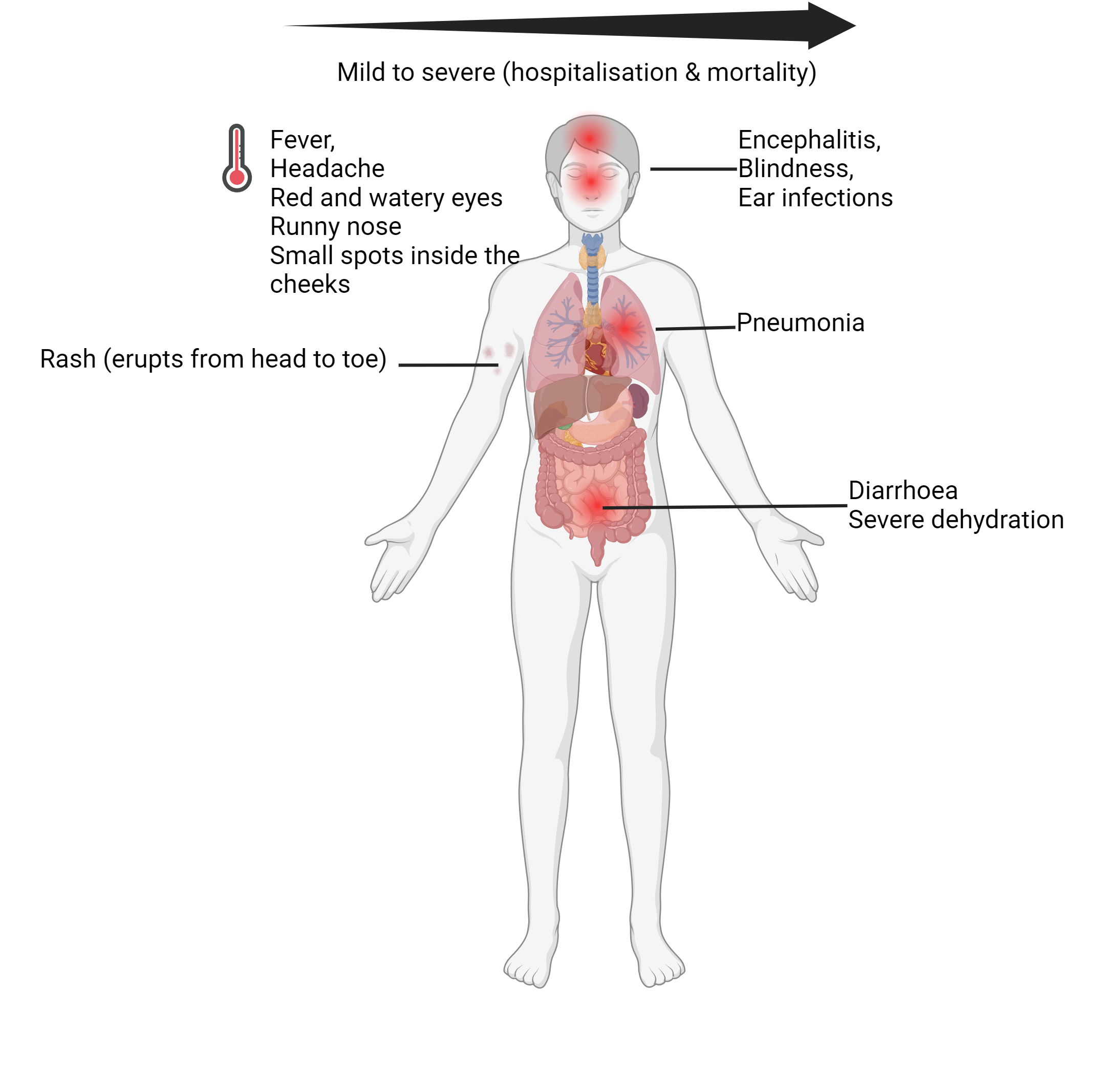
Hospitalisation occurs in 1 out of 4 unvaccinated people who gets measles.
Mortality occurs about 1 or 2 out of 1000 unvaccinated people with measles.
Serious complications are common in children under 5 years old and over 30 years of age.
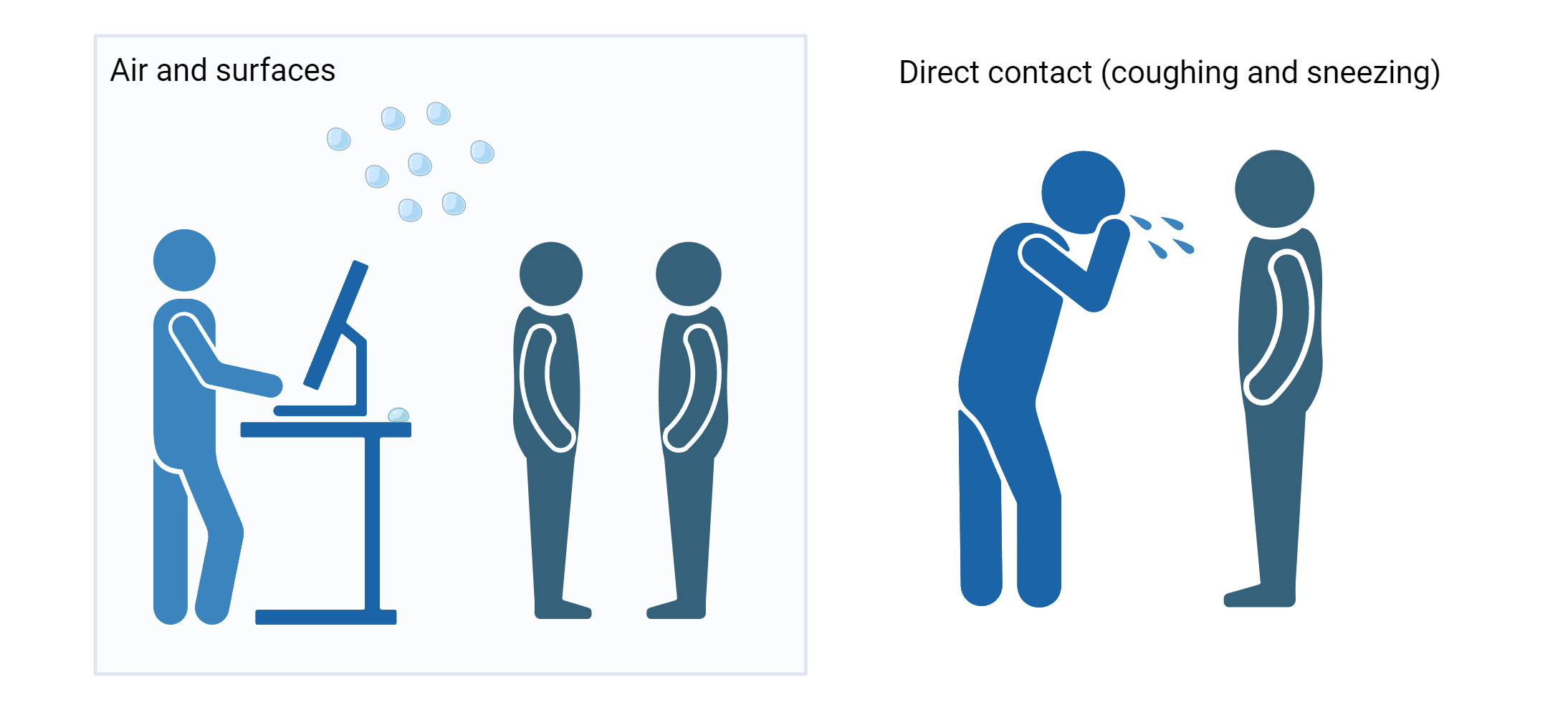
Measles is one of the world’s most contagious diseases
Measles is normally passed through direct contact (coughing or sneezing) and the air
The virus remains active and contagious in the air or on infected surfaces for up to two hours
Transmission occurs from four days prior to the onset of the rash to four days after the rash erupts